Computational Methods for Social and Behavioral Scientists
Published:
Salganik, M. (2018). Bit By Bit
## Computing Revolution > - The cost of storing and analyzing data has plummeted ## Computing Revolution ## What is Computational Social Science? > - Broadest version: using computers to help with social science research > - Could include statistical and visualization software, Qualtrics, etc. > - I'll focus on using computational tools that enable new kinds of research ## Data Science vs. Computational Social Science > - Imagine some sort of social process; we might represent it as: > - $\hat{Y} = \mathbf{\hat{\beta}} \mathbf{X} + \epsilon$ > - Data science (and particularly machine learning) is often interested in prediction > - Caring about $\hat{Y}$ rather than $\hat{\beta}$ > - Computational social science is typically interested in explanation and understanding (correctly estimating $\hat{\beta}$) ## Data Science for Social Scientists > - Sometimes scientists are interested in prediction > - E.g., Classifying people or texts > - Machine learning methods can also be used for: > - Reducing dimensionality > - Avoiding overfitting > - Generating hypotheses ## Discussion Pause > - Are there ways that machine learning is used in your field? > - Are there ways that you think it could be? # Examples of Computational Social Science ## Large-scale analyses ## Large-scale analyses - Goel et al. looked at over 1 billion tweets to study how information spreads 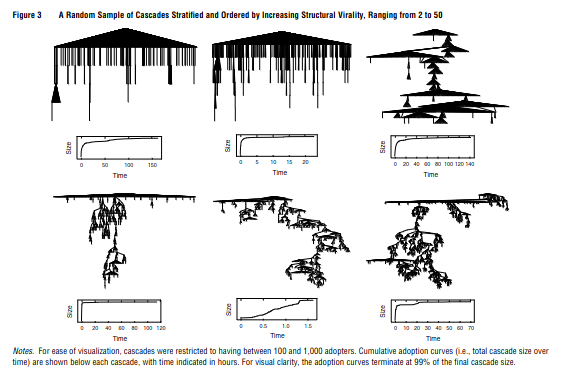 ## Large-scale analyses > - Really important opportunities for studying groups, which are often expensive and difficult to study > - E.g., Our paper looking at the early-stage structures of ~1,000 wiki communities ::: notes - Not only a huge number of communities, but at early stages. Only possible because of always-on data ::: ## Social Network Analysis {background-image="https://jeremydfoote.com/images/FacebookSNA.jpg" background-opacity="0.08"} > - Studying outcomes in terms of relationships > - Doesn't assume that people are independent > - Statistical methods are complex and computationally expensive ## Computational Text Analysis > - Reading and analyzing texts takes a long time! > - Automated methods can quickly analyze vast amounts of text > - Inductive methods (unsupervised) > - Topic modeling > - Word embeddings ## Computational Text Analysis > - Deductive methods (supervised) > - Sentiment analysis > - Named entity recognition > - Classification ## Agent-based Modeling > - Using theory, develop of model of how individuals make decisions > - Simulate what happens when many individuals interact## Discussion Pause > - Any questions about these methods? > - Are there ways that you think these methods could be used in your field? ## Large-scale field experiments run by computers ::: container ::: col
## Large-scale analyses > - Really important opportunities for studying groups, which are often expensive and difficult to study > - E.g., Our paper looking at the early-stage structures of ~1,000 wiki communities ::: notes - Not only a huge number of communities, but at early stages. Only possible because of always-on data ::: ## Social Network Analysis {background-image="https://jeremydfoote.com/images/FacebookSNA.jpg" background-opacity="0.08"} > - Studying outcomes in terms of relationships > - Doesn't assume that people are independent > - Statistical methods are complex and computationally expensive ## Computational Text Analysis > - Reading and analyzing texts takes a long time! > - Automated methods can quickly analyze vast amounts of text > - Inductive methods (unsupervised) > - Topic modeling > - Word embeddings ## Computational Text Analysis > - Deductive methods (supervised) > - Sentiment analysis > - Named entity recognition > - Classification ## Agent-based Modeling > - Using theory, develop of model of how individuals make decisions > - Simulate what happens when many individuals interact## Discussion Pause > - Any questions about these methods? > - Are there ways that you think these methods could be used in your field? ## Large-scale field experiments run by computers ::: container ::: col - Facebook's election study - Inivited 14.6 million users to participate - ~76K participants
- Our experiments on toxicity and chatbots - Behavior _before and after_ participating
::: ::: col 
::: ::: ## Citizen Science > - Pre-computers, organizing data was incredibly expensive and difficult {.center}
## Citizen Science > - Today, we can organize the work of thousands of people fairly easilty > - iNaturalist > - Galaxy Zoo > - Protein folding > - SETI@home ## Generative AI tools > - _Lots_ of current research on LLMs > - How will LLMs become part of the social world? > - LLMs as tools for social science research > - Brainstorming partners > - Research assistants (e.g., summarizing papers, classifying texts) > - Editors / reviewers > - Blurring the line betweeen method and collaborator ## Discussion Pause > - Any questions about these methods? > - How are you using AI in your current research workflow? ## Ethical concerns of Computational Social Science > - People are often unaware of how their data are being used, even if it is "public" > - Data can be used by bad actors > - Really important to balance privacy and research goals ## Methodological concerns of Computational Social Science > - Hard to do, especially for really large-scale analyses > - Algorithmically confounded > - Data may be missing or biased in invisible ways > - Data collection processes may change over time in invisible ways > - Nonrepresentative samples ## Learn More > - Salganik, M. (2018). Bit By Bit > - Take my class (Spring 2026) # Optional activity ## Design a study that uses computational methods to study a question you are interested in